PECULIARITIES OF ADMINISTRATION OF BUSINESS PROCESSES AT THE ENTERPRISE
УДК 658.5
Глєбова А., к.е.н., доц.
Маховка В., к.е.н., доц. кафедри туризму та адміністрування
Полтавський національний технічний університет імені Юрія Кондратюка
Анотація: У статті розглянуто теоретичну сутність і значення терміна “адміністрація”. Адміністрування підприємств розглядається з точки зору процесуального підходу та орієнтовано на опис, регулювання, постійне відстежування бізнес-процесів, які підлягають корегуванню у разі виявлення помилок впровадження або відхилень від результатів. Автори виділяють два підходи до адміністрування бізнес-процесів, які доцільно використовувати на підприємствах: вдосконалення існуючих бізнес-процесів та їх реінжиніринг.
Ключові слова: адміністрація, бізнес-процес, реінденсинг, бенчмаркінг, ресурси.
Abstract: The article deals with the theoretical essence and meaning of the term “administration”. The administration of enterprises is considered from the viewpoint of the process approach and focused on business processes that are described, regulated, are constantly monitored and subject to adjustments in case of implementation errors detection or deviations from the results. The authors distinguish two approaches to the administration of business processes, which are advisable to use at enterprises: improving existing business processes and their reengineering.
Keywords: administration, business process, reindeniring, benchmarking, resources.
The dominance of innovation development concept in the post-industrial economic theories defines the strategic priorities in management of most enterprises. Including the industry companies with target objectives and tasks focused on innovation development. Ander the conditions of looking for ways out of the current transformational enterprises crisis, an important and urgent task is to develop a systematic approach to the formation of mechanism of it management and administration.
Today, for enterprises engaged in activities, it is urgent to address the problems of increasing competitiveness and retaining leadership in their market sector. The main goal of the activity of any enterprise is to increase the efficiency of the business. Achieving this goal can be facilitated by effective administration of business processes. In this case, the orientation of companies on business processes is due to the active introduction of automatic management into practice. An important condition in this case is not only the establishment of business processes as one of the areas of work with the internal environment, but also bringing them in line with the rapidly changing requirements of the external environment.
Administration should be considered as an activity aimed at a systematic approach to step-by-step and coordinated organization of all management processes and aspects of the enterprise’s operation with the aim of: rhythmic work of the organization; satisfaction of consumers’ desires and observance of high growth rates of sales volumes; formation and observance of a positive image of the enterprise; effective use of all types of resources, interaction with public, trade union and government institutions; providing motivation; increase professionalism and conditions for career growth of employees in the process of achieving the goals of the organization and the growth of the company’s status.
In any understanding of process management, the management of the business process in the direction of its improvement (improvement) is the fundamental and decisive factor in improving management efficiency. Two approaches to the administration of business processes can be distinguished, which should be used at enterprises.
The first involves improving existing business processes, and the second involves redesigning business processes and reengineering them. Improvement of business processes can lead to a noticeable improvement, but only to increase in relation to the existing level of business. Such improvement occurs due to the abandonment of secondary activities, the reformatting of structural units and the delegation of authority with the aim of increasing efficiency and saving the resources used. In contrast to this improvement, redesigning processes, in particular, reengineering, involves radical, fundamental changes. This can mean restructuring both individual processes, and the organization as a whole, as well as relationships with suppliers and consumers. Such restructuring is carried out after careful analysis of existing business processes and rethinking of new ways of their effective interaction.
The concept of business process improvement (Business Process Improvement) is based on four approaches aimed at increasing the productivity, efficiency and adaptability of business processes (Fig. 1) [1].
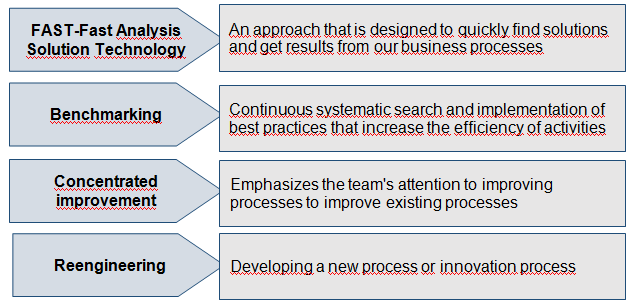
Fig. 1. Business process improvement Concept
FAST rapid analysis methodology is an approach that is designed to quickly find solutions and obtain results from our business processes. A methodology for rapid analysis of FAST solutions from the point of view of managing business processes for enterprises focused on focusing attention of individuals who administer the process in a certain process during a one-two-day meeting to determine the ways in which the group can improve this process within the next 90 days. Before the end of the meeting, the administration approves or rejects the proposed improvements. This methodology can be used in events of any level, starting with the main processes and ending with the level of the event. An example for improvement when using the FAST approach is to reduce costs, cycle time and error rate by 5-15% [2].
Also at companies, in order to improve the administration of business processes, it is advisable to use the benchmarking method, taking the experience of Xerocc, which used it to radically change its strategy and received the Malcolm Baldrige award for it. This type of activity can be called a comparative analysis. Benchmarking process is a systematic method of determining, understanding and creative development of goods, services, projects, equipment, processes and procedures (established principles) of higher quality to improve the current activity of the company by examining how different companies perform the same or similar operations. Typically, benchmarking reduces costs, cycle time and error rate by 20-50%. During benchmarking, alternative solutions are provided (with the help of comparative analysis) that can lead to improved business processes, and choose the one that will bring the best result from the perspective of the company’s future perspective (BFSS – Best-Value Future-StateSolution). Future-oriented solution (FSS) is a combination of corrective actions and changes that can be applied to the process under investigation to increase its value for shareholders. The most beneficial future-oriented solution (BFSS) leads to the most profitable redesign of the business processes of the enterprise from the perspective of shareholders. This solution characterizes the optimal ratio of the required cost combinations, the duration of the implementation cycle, the risk and the result, for example, return on investment, customer satisfaction, market share, risk, value added per worker, implementation time, implementation costs, and the like. When implementing a standard benchmarking project, the development of the most profitable, future-oriented solution takes 4 to 6 months. Given the experience of using this approach, it is advisable to choose for 5-20% of the company’s core processes [3].
The redesign process (concentrated improvement) focuses the attention of the Process Improvement Team (PIT) on improving existing processes. As a rule, redesign is applied to those processes that function quite successfully and at the moment. Redesigning processes reduces costs, cycle time and error rate by 30-60%. When redesigning the definition process, BFSS takes between 80 and 100 days. The use of this approach in enterprises can be correct for approximately 70-90% of the main business processes. Such an approach is advisable to use if improving the performance of the enterprise by 30-60% can provide it with competitive advantages.
Reengineering of the process is also called the development of a new process or the innovation of a process, since its success is mainly based on the innovations and creative abilities of the team to improve the processes of the RIT. He is the most radical of all four approaches to improving business processes. This approach provides a fresh look at the goals of the process and completely ignores the existing process and the structure of the company, it all starts “from scratch”, as if you are just beginning to develop this process. Reengineering, if carried out correctly, reduces the costs and cycle time by 60 to 90% and the error rate by 40–70% [3].
In our opinion, business processes should be understood as a system of continuous, interrelated, appropriately ordered and managed actions (procedures, operations, performed functions), which, in turn, is an element of the mechanism of formation of value added (consumer value) through the transformation of organizational resources , focused on achieving one common goal, which is aimed at ensuring the productivity and effectiveness of the organization as a whole and providing an added value report spine (consumer value) to the target market through the business model of the enterprise. Effective administration of business processes at ompanies will ensure: determining the optimal sequence of functions that leads to a reduction in the cycle of manufacturing and selling goods and services, customer service, resulting in increased capital turnover and growth of all economic indicators of the company; optimize the use of resources in various business processes, as a result of which the costs of production and circulation are minimized and the optimal combination of various activities is ensured; building adaptive business processes aimed at rapid adaptation to changes in the needs of end-users, the process, the behavior of competitors in the market and, accordingly, improving the quality of customer service in a dynamic environment; definition of rational schemes of interaction with partners and clients, and, as a result, profit growth, optimization of financial flows.
REFERENCES
Mohamed Zairi, David Sinclair, (1995) “Business process re‐engineering and process management: a survey of current practice and future trends in integrated management”, Management Decision, Vol. 33 Issue: 3, pp. 3-16.
N.R. Jennings, P. Faratin, M.J. Johnson, T.J. Norman, P. O’brien, and M.E. Wiegand AGENT-BASED BUSINESS PROCESS MANAGEMENT, International Journal of Cooperative Information Systems, June 1996, Vol. 05, No. 02n03: pp. 105-130.
R.G. Lee, B.G. Dale, (1998) “Business process management: a review and evaluation”, Business Process Management Journal, Vol. 4 Issue: 3, pp.214-225.